The Complete Guide to Medicare
Navigating Medicare may seem overwhelming at first, but it doesn’t have to stay that way. This guide provides a clear explanation of what
Medicare is, outlines each stage of the Medicare journey, and highlights important steps to follow.
You’ll also learn how to avoid common mistakes so you can make smarter, more confident decisions.
Why Medicare Matters
For millions of Americans, Medicare marks a major milestone in their healthcare journey. Whether you’re nearing retirement, supporting a loved one, or seeking coverage due to disability, Medicare provides access to vital healthcare services and protection from high medical costs.
This guide will help you understand what Medicare is, when and how to enroll, and which options may best fit your needs.
What Is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for Americans age 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities or End-Stage Renal Disease. It covers essential healthcare services, ensuring millions of beneficiaries receive medical care when they need it most.
Medicare vs. Medicaid
Although their names sound alike, these programs are different:
• Medicare: Federal program primarily for seniors and certain disabled individuals, regardless of income.
• Medicaid: Joint federal and state program for low-income individuals and families of all ages.
*Some people qualify for both (called dual eligibility), which provides more complete coverage.
Start Your Medicare Conversation
Book a free call below—or if you’re ready now, give us a call at (833) 854-5745.
When Am I Eligible?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for Americans age 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities or End-Stage Renal Disease. It covers essential healthcare services, ensuring millions of beneficiaries receive medical care when they need it most.
How to Enroll in Medicare
There are two paths to enrollment:
• Automatic Enrollment: If you’re already receiving Social Security benefits, you’ll be enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B automatically. Your card will arrive about three months before your 65th birthday.
• Self-Enrollment: If not automatically enrolled, you must sign up during your Initial Enrollment Period (IEP) — a 7-month window surrounding your 65th birthday.
Do You Have to Enroll at 65?
Not always. If you’re still working and have employer coverage (or coverage through a working spouse), you may be able to delay Medicare without penalties. The rules vary, so it’s important to review your situation carefully.
Understanding Your Medicare Number
Your Medicare card displays a unique, randomly generated number used for claims and benefits — replacing the old Social Security–based system for better security.
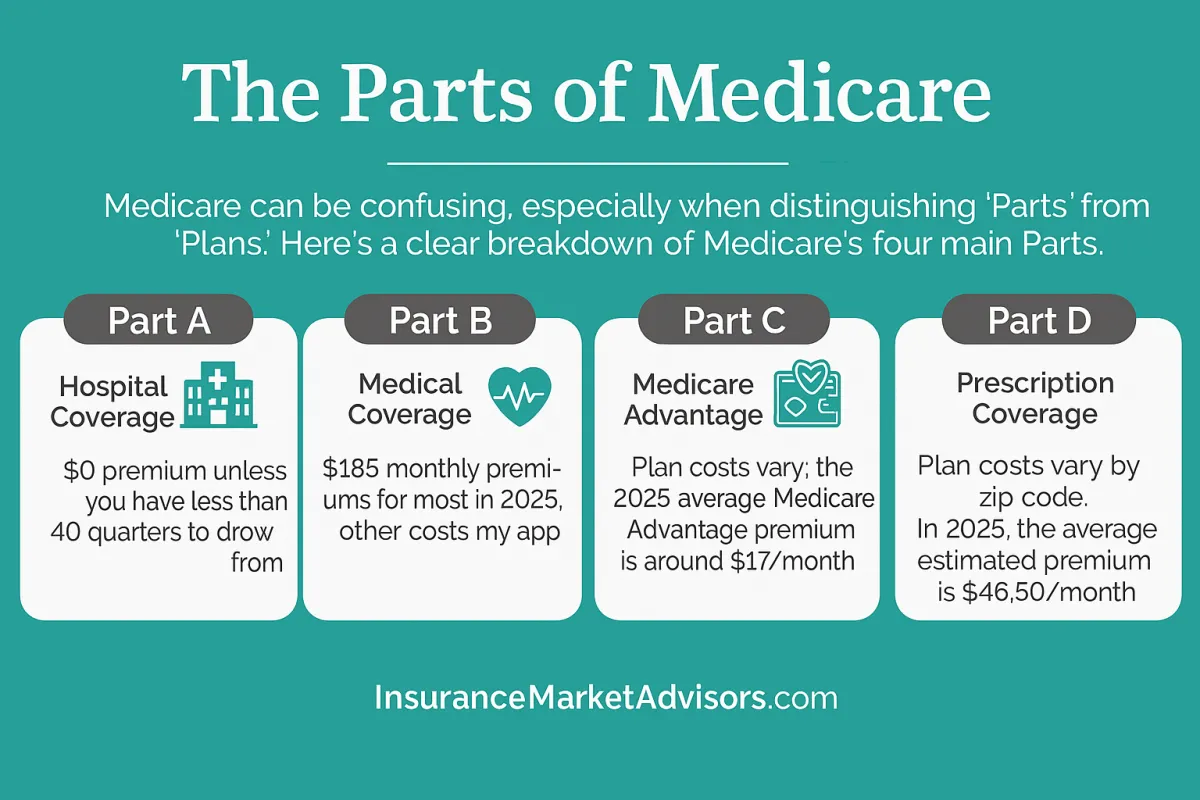
The Parts of Medicare
Medicare is divided into four parts:
• Part A (Hospital Insurance) – Inpatient care, skilled nursing facilities, hospice, and some home health care.
• Part B (Medical Insurance) – Doctor visits, outpatient care, preventive services, and durable medical equipment.
• Part C (Medicare Advantage) – Private plans that bundle Parts A and B, often including vision, dental, hearing, and prescription drugs.
• Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage) – Helps cover the cost of medications, offered as standalone or within Part C plans.
Costs of Medicare
Medicare is not free. Costs include premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
• Part A: Usually no premium if you or your spouse paid Medicare taxes for 10+ years. Deductible in 2025 is $1,676 per benefit period, with coinsurance for longer hospital stays.
• Part B: Standard premium in 2025 is $185/month (higher for higher incomes). Annual deductible is $257, after which you pay 20% of Medicare-approved services.
Filling the Gaps in Original Medicare
Original Medicare (Parts A & B) leaves beneficiaries responsible for out-of-pocket costs. Two main options can help:
• Medigap (Supplemental Insurance): Private plans that pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
• Medicare Advantage (Part C): An alternative that replaces Original Medicare, often adding drug, dental, and vision coverage.
Important: You cannot have both Medigap and Medicare Advantage. You must choose one.
Prescription Drug Coverage (Part D)
Helps pay for medications, with costs and covered drugs varying by plan. Drugs are grouped into tiers, each with different copays or coinsurance.
Vision & Dental Coverage
Vision & Dental Coverage
• Original Medicare: Limited coverage (primarily medical conditions like cataracts or glaucoma).
• Medicare Advantage: Many plans include routine eye exams, glasses, and dental benefits.
Getting Help With Medicare
Medicare can feel overwhelming — but you don’t have to figure it out alone. Licensed insurance agents and brokers can explain your options, compare plans, and help you enroll at no cost to you (they’re paid by insurance companies).
You can also attend Medicare seminars or virtual workshops to learn from experts and ask questions in real time.
Take the Next Step
Medicare is flexible, but choosing the right coverage requires understanding your healthcare needs, financial situation, and provider preferences. With the right guidance, you can avoid costly mistakes and secure the coverage you deserve.
👉 Schedule a free call today to speak with a Medicare guide and get personalized advice.
Copyrights 2024| Insurance Market Advisors™ | Terms & Conditions